Before we dive into how to lower estrogen through the gut, it's important to understand what drives estrogen up in the first place, especially in men. Most people blame high estrogen on genetics or age, but in reality, it’s often the result of chronic inflammation, liver dysfunction, poor bile flow, and microbiome imbalance.
Here are the major contributors:
1. Aromatase Activation
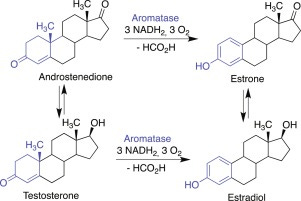
Aromatase is the enzyme that converts testosterone into estrogen. When it’s overactive, estrogen rises while testosterone drops, causing a double hit to your hormonal balance.
What increases aromatase?
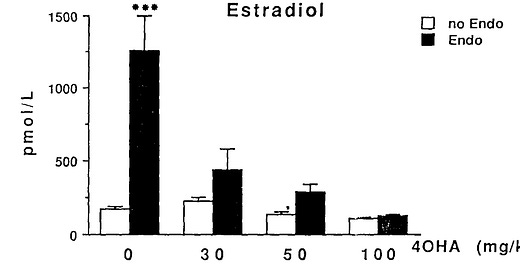
Endotoxin (LPS) – Produced by gram-negative bacteria in the gut. A major trigger of inflammation and aromatase expression.
Inflammation – IL-6, TNF-α, and other inflammatory cytokines upregulate aromatase.
Cortisol – Chronic stress raises cortisol, which promotes aromatase.
Histamine – High histamine levels (often from gut-derived mast cell activation) can increase aromatase, shown clearly in women, and likely in men too (R).
Nutritional deficiencies – Zinc, magnesium, selenium, and vitamin D all play a role in suppressing aromatase. Deficiencies remove this brake.
Low T3 (thyroid hormone) – T3 suppresses aromatase, so hypothyroid men often have a high estrogen-to-testosterone ratio despite “normal” labs.
If your inflammation is high and your T3 is low, your testosterone will get hijacked and converted to estrogen.
2. Poor Estrogen Detoxification via the Liver
Your liver is responsible for metabolizing and clearing estrogen. This involves two main steps:
Phase I:
Enzymes like CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 convert estrogen into intermediate metabolites (e.g., 2-OH-E1, 4-OH-E1).
Phase II:
These intermediates are conjugated (methylated, sulfated, or glucuronidated) into water-soluble forms and sent out via urine or bile.
If your liver lacks the necessary enzymes, nutrients, or energy, this system backs up. This leads to a build-up of:
More potent estrogens (like estradiol)
Toxic intermediates (like 4-OH-E1 and 16-OH-E1)
Estrogen dominance symptoms
Without proper liver support, even normal estrogen levels can cause problems due to poor clearance.
3. Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance promotes estrogen dominance in several ways:
Increases aromatase activity in fat tissue
Reduces SHBG, increasing free estrogen
Worsens liver detox (since insulin resistance promotes fatty liver)
And what’s one of the key drivers of insulin resistance?
👉 Endotoxin.
Endotoxin promotes:
Liver inflammation (via Kupffer cell activation)
Hepatic insulin resistance
Fatty liver (NAFLD)
Inflammation-driven estrogen buildup
Studies show that just a small rise in LPS levels can cause a rapid increase in:
Liver TNF-α
Hepatic fat accumulation
Aromatase activity
So if your gut is inflamed and leaking LPS into your liver via the portal vein, your estrogen will climb—even if your testosterone production is solid.
4. Poor Bile Flow
Once your liver detoxifies estrogen, it sends it into the bile for elimination. If bile flow is sluggish:
Estrogen stays stuck and gets reabsorbed in the intestines
Bile’s antimicrobial action drops → gram-negative bacteria overgrow
This creates a vicious cycle of more LPS, more inflammation, more aromatase
Bile is the body’s waste chute. If it clogs up, estrogen builds up fast.
5. Beta-Glucuronidase Overactivity
Even when your liver does everything right, certain bacteria can sabotage the process.
Beta-glucuronidase breaks the glucuronic acid bond on conjugated estrogen, allowing it to re-enter your bloodstream.
It’s highest in:
Dysbiosis
Constipation
Low-fiber diets
Inflammation-driven microbiome shifts
This enzyme silently blocks detox and keeps estrogen circulating longer than it should.
Now let’s discuss how to optimize each of these in depth.