Allopregnanolone - the neurosteroid you need more of
From Social Resilience to Depression Relief—Allopregnanolone Helps It All
Why You Should Care About Allopregnanolone
If you’ve ever felt deep calm from breathwork, better mood after a glass of wine, or heightened mental clarity following high-fat meals or pregnenolone use, you’ve likely experienced a boost in allopregnanolone—whether you knew it or not.
Allopregnanolone (AlloP) is not just another neurosteroid. It’s one of the most powerful mood, cognition, and nervous system modulators your body can produce. And unlike benzos or synthetic sedatives, AlloP heals as it calms.
It doesn’t just sedate your brain—it rewires it for emotional resilience, fear extinction, sleep restoration, and even better mitochondrial function.
Yet it’s often depleted in conditions like:
PTSD
Depression
Social isolation
Post-finasteride syndrome (PFS)
Alzheimer’s (R)
Chronic stress and inflammation
That makes it a core pillar for mental performance, hormone health, and recovery.
In this article, we’ll break down:
How it’s made
What it actually does inside your brain and body
Every major benefit it provides
Natural strategies to increase it
Pharmaceutical options like topical or injectable AlloP
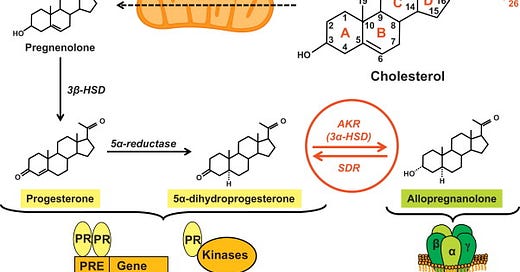
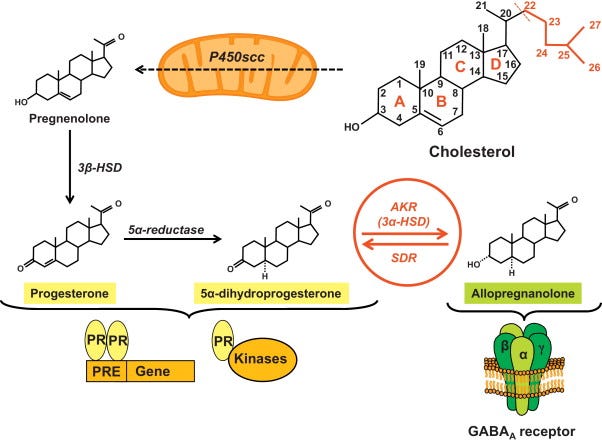
How Allopregnanolone is Made
Allopregnanolone is a downstream metabolite of progesterone, but its synthesis depends on two key enzymes:
1. 5α-reductase (type 1 & 2)
Converts progesterone into 5α-dihydroprogesterone (5α-DHP).
2. 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3α-HSD)
Converts 5α-DHP into allopregnanolone.
This all happens in the brain (especially cortex, hippocampus, amygdala), adrenal glands, and even Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. It’s synthesized de novo, meaning your brain doesn’t rely on ovaries or testes to get it.
But here's the problem:
Stress, inflammation, and social isolation downregulate these enzymes.
This reduces AlloP production, even if you have plenty of progesterone floating around.
That’s why you can be low in AlloP even if your hormones look "normal" on paper.
Also critical:
AlloP synthesis is mitochondrial-dependent. PEA (palmitoylethanolamide) and PPAR-α activation increase StAR protein and P450scc, both required for steroidogenesis in glial cells.
Mechanisms of Action (MOA)
Here’s where it gets exciting.
Allopregnanolone acts on multiple systems simultaneously, but its core effects stem from:
1. GABAA receptor modulation
It’s a positive allosteric modulator, like benzodiazepines—but with 20x more potency and broader receptor subtype activity.
Binds especially to δ-subunit-containing GABAA receptors (extrasynaptic), promoting tonic inhibition and deep calm.
No tolerance buildup, no rebound anxiety.
2. Inhibition of CRH and cortisol
AlloP suppresses CRH gene expression and ACTH release, blunting the HPA axis.
It’s your body’s natural “off switch” for the stress response.
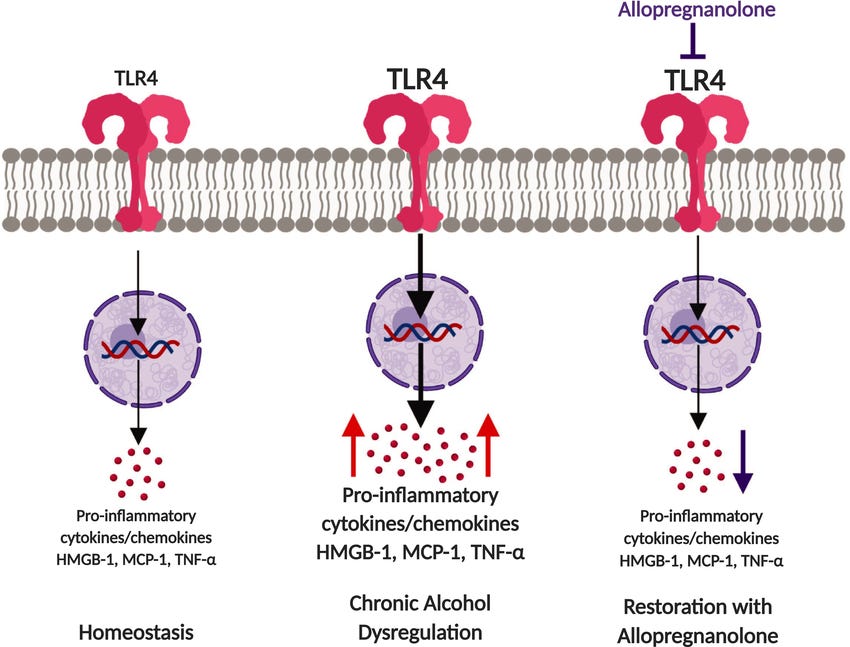
3. Neuroinflammation control
AlloP inhibits TLR4 signaling, reduces microglial activation, and lowers pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6).
Especially protective in models of Alzheimer’s, stroke, and multiple sclerosis.
4. Dopamine & glutamate system enhancement
Boosts dopaminergic tone (via D2 receptors), restoring motivation and pleasure.
Enhances GAD expression and glutamate uptake in glial cells, reducing excitotoxicity.
5. Mitochondrial protection
Increases Complex I and II respiration.
Reduces calcium overload and ROS from inflammatory insults like HIV Tat protein.
AlloP is not just a calming molecule. It’s a multi-modal neuroprotective repair signal, dialing down hyperarousal while enhancing cellular function.
The Full List of Benefits of Allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone is one of the few molecules in the body that works on both mood and mitochondria, neuroinflammation and motivation. Below is a breakdown of its full spectrum of benefits, categorized by system:
Mental Health & Emotional Stability
Anti-anxiety – AlloP powerfully reduces anxiety via GABAA potentiation, even in high-stress models (R).
Antidepressant – Effective in both postpartum and major depression; normalizes firing in dorsal raphe serotonin neurons.
PTSD recovery – Facilitates fear extinction and lowers amygdala hyperactivity; low CSF AlloP is strongly linked to PTSD severity (R).
Anti-aggression – Reverses isolation-induced aggression by restoring corticolimbic AlloP.
Loneliness resilience – Supports HPA regulation and inflammation control under socially isolating conditions.
Neuroprotection & Cognitive Support
Protects against Alzheimer’s – Inversely correlated with Braak stage; suppresses neuroinflammation and supports mitochondrial function.
Improves memory – Enhances hippocampal function and normalizes glutamate/GABA ratios.
Reduces neuroinflammation – Inhibits TLR4/7 signaling; reduces microglial reactivity and lymphocyte infiltration.
Restores circadian rhythm – Increases hypothalamic AlloP and normalizes activity amplitude in aging models (R).
Motivation, Energy & Dopaminergic Tone
Boosts dopamine – Enhances D2 receptor activation, improves reward sensitivity and motivation.
Normalizes glutamate – Increases GAD (GABA-producing enzyme) and glutamate uptake via EAAT1.
Restores pleasure drive – Works in learned helplessness and depression models to restore behavior and motivation.
Hormonal & HPA Axis Modulation
Suppresses cortisol – Reduces CRH and ACTH expression; acts as a brake on the stress response.
Counters post-finasteride syndrome (PFS) – Reverses low AlloP, inflammation, and serotonin/dopamine imbalance (R).
Modulates estrogen/testosterone signaling – Likely via feedback effects on upstream hormones.
Mitochondrial Health & Energy Metabolism
Protects against oxidative stress – Attenuates ROS production in neurons and astrocytes.
Increases mitochondrial respiration – Enhances Complex I & II activity (R).
Rescues mitochondrial function after injury – Protects against HIV Tat protein, ischemia, and other insults.
Sleep & Recovery
Improves sleep quality – Increases deep sleep, reduces REM latency, counters sleep deprivation effects.
Reduces sleep fragmentation – Especially under stress, isolation, or inflammatory conditions.
Pain & Analgesia
Analgesic – Inhibits T-type calcium channels and amplifies GABAA signaling to reduce pain perception.
Allopregnanolone doesn’t work like a band-aid. It rebuilds the underlying neurobiology of calm, resilience, and motivation.
Now let’s talk about how to increase it naturally, and what other solutions there are to maxx out your alloP.